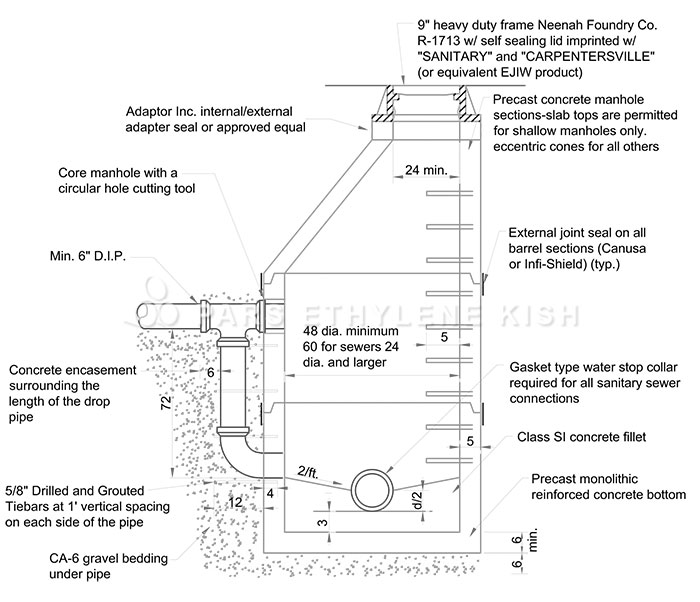
Polyethylene Drainage Manhole
Sewage Manhole
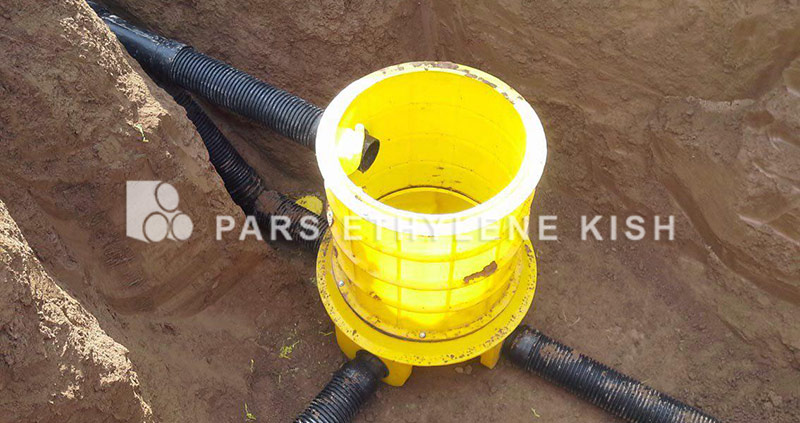
Drainage manholes ( chamber in drainage )are used on sloping surfaces and have inlet and outlet pipes, which are used in such a way that the converter pipes have a higher height and reduce the slope of the surfaces.
Polyethylene drainage manhole (chamber in drainage)
When the flow of a sewage is connected to other sewage, if the surface difference between these sewage is high and the water level in the main sewage at its highest position is greater than 0.6 meters, then the manner of the drainage manhole structure is like the drainage pipe and completely vertical or almost vertical, and sewage is classified from top to bottom. A drainage manhole is also used on sloping surface sewage lines, when drainage is more than 0.6 m, we need to control the slope to reach the required speed.
inspection chamber in drainage system and Internal structure of polyethylene drainage manhole
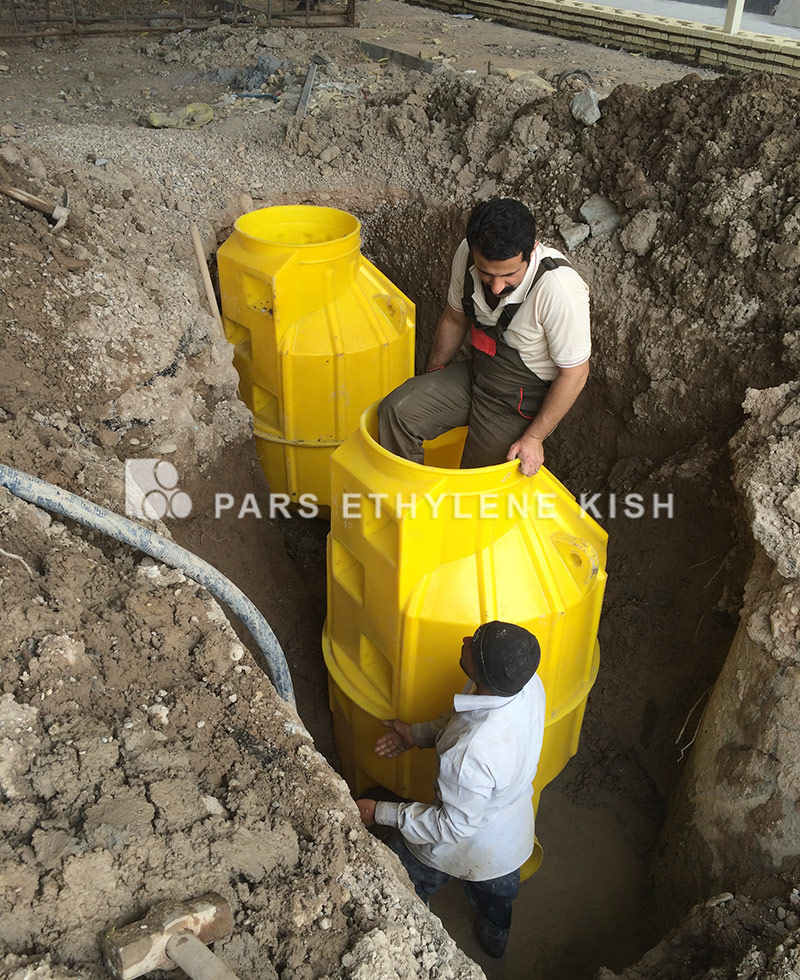
The internal structure of the drainage manhole ( chamber in drainage ), in which the pipes are mechanically connected to the walls, are different from the manhole that the input pipes are tied by manpower, which is the difference of about 26 inches (600 mm) or more. There is also a different type of engineering design in this type of manhole, including the reduction of SH emission, unpleasant odor, sewage confusion in the manhole channel, and the prevention of wear and corrosion of the internal structure of the manhole.
The settings must be such that each piece of the product can rotate and the door can be separated from the pipes.
-
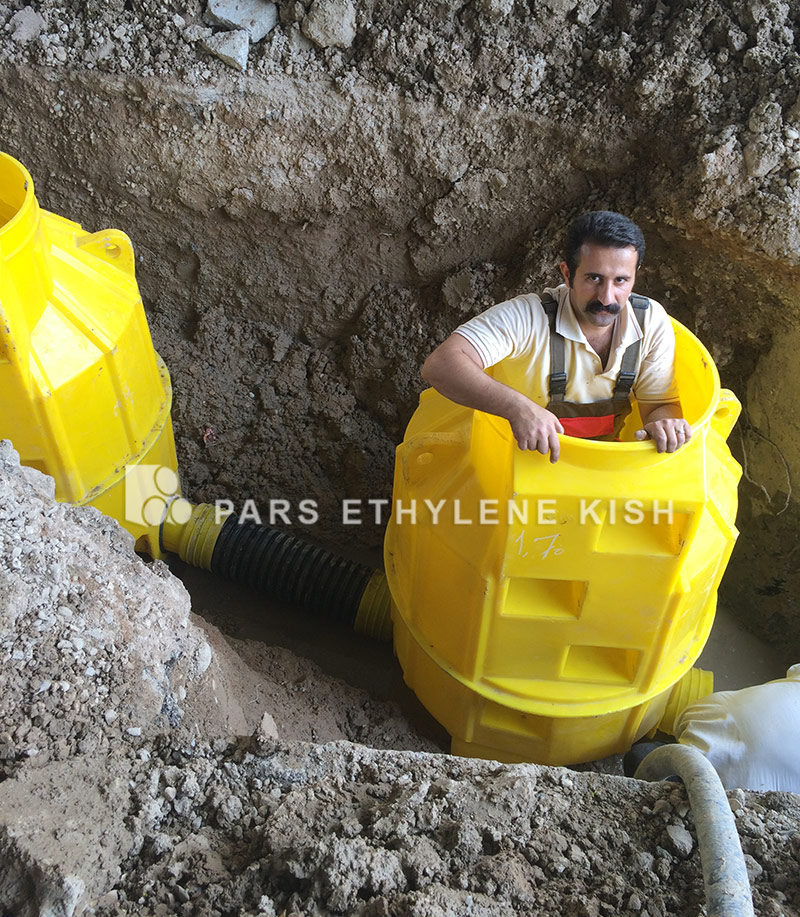
1. The fittings should be fitted with inlet pipes and have a diameter of about 10 inches (250 mm). The end of the fitting must accept the final gaskets of SDR26PVC SDR / 635 or 8 and the gravity sewage pipe should be horizontally placed inside it to allow flow into the manhole.
-
2. The interior structure of the door may be removed to create an empty area and may be attached to the body with an iron stainless steel chains to prevent losing the door.

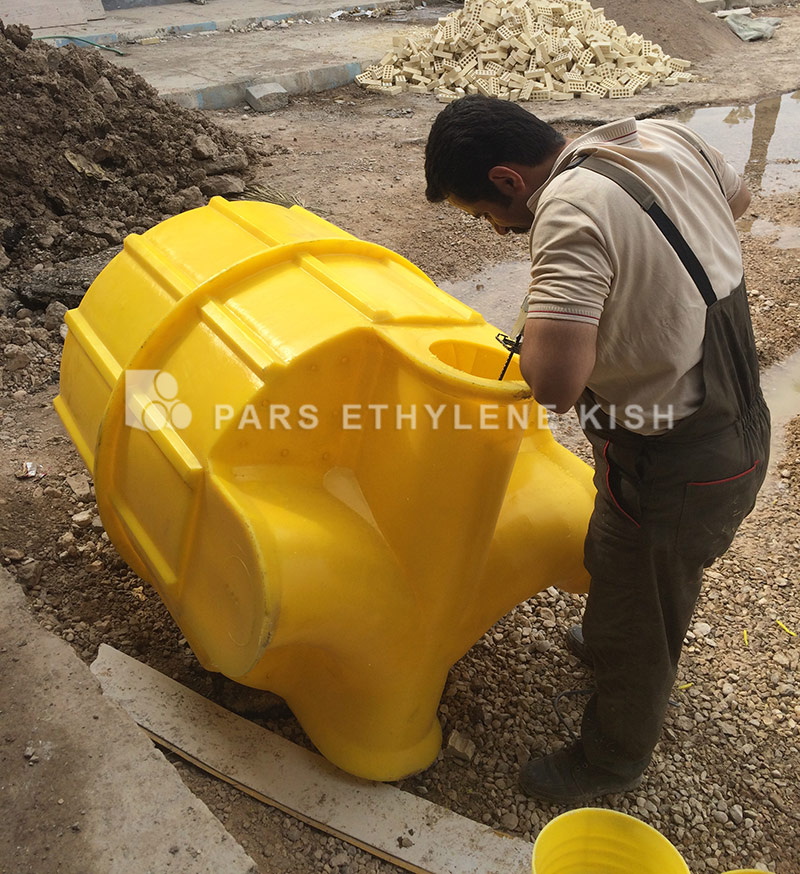
Polythene drainage manhole material
-
Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) body
-
Door of high density polyethylene (HDPE)
Drainage manhole fittings
Drainage manhole fittings should be based on the standards / 1.3.1 S and / a3.1 S with a diameter of 2.47 meters for sewage pipes; / B3.1 S and / C3.1S can also be used for sewage of 20 cm diameter. If other sizes are used, special designs should be applied. Larger sewer pipelines do not usually have a pre-predicted design because it may require more space.
Drainage manholes have splittings, and these divisions are based on tube design. In order to use the fittings for pipes, it is first necessary to check the pipes and select the drainage manhole fittings of the same type with the pipes.
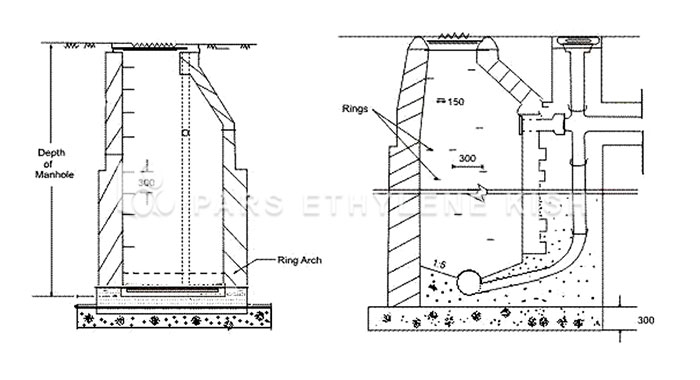
inspection chamber in drainage system
Energy dissipation in circular drainage manhole in different outlet flow
Drainage manhole ( chamber in drainage ) is an important tool in reducing the speed and eliminating the energy of urban sewage networks. The loss of energy in the drainage manhole depends on the manhole flow pattern in the outlet pipes and downstream forces, and is similar to the manhole's hydraulic and geometric parameters. The loss of manhole energy dissipated with sample diameters is investigated. Finally, energy dissipation is considered when cooling the system.
Drainage manhole ( chamber in drainage ) has a hydraulic feature that is widely used in urban sewage networks in sloping ponds. The loss of energy in the drainage manhole is one of the major concerns of in-city systems designers. There should be a certain amount of energy loss in the falling manholes to prevent excessive water velocity in the outlet pipes. However, this is not always feasible, as widespread waste disposal takes place in a sewage system during floods.
The energy loss in the drainage manhole ( chamber in drainage ) is related to several factors, which can be classified into three categories:
-
1. The flow conditions are generally related to the ratio of the upper tube filling and the flow approach.
-
2. The flow conditions, for example, the free flow rate, which includes free-flow and pressure-flow, limits the flow, which reverses the effects of groundwater on the outlet pipe. Manhole configuration and dimensions, which include input and output settings.