|

Sub-Drains
A subdrain system is an underground network of piping used to remove water from areas that collect or retain surface water or groundwater. The network can be rather small, such as might be used to drain a limited area, or fairly large to drain a sizeable number of acres.
Surface water can be collected into the subdrain system by installing a surface inlet or catch basin. Groundwater is collected by allowing water into the pipe through perforations. Both surface water and groundwater can be discharged to an appropriate outlet such as a nearby storm sewer, pond, or river.
The effectiveness of a subdrain system is determined 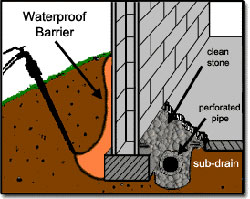 by the native soil, spacing, and depth of the pipe, as well as its diameter. It is important to determine specifically why a site needs improved drainage. Does the area contain plants that will be damaged it their roots are submerged? Is the area used for parking or recreation and must be useable even shortly after a rain? Answers to questions such as these will help determine how deep the pipe should be buried, how close together the laterals should be placed, and the pipe size and slope. The native soil is also a major factor in the system layout. Tight clay soils do not release groundwater as readily as looser sandy soils so a different layout will be required for a similar response. by the native soil, spacing, and depth of the pipe, as well as its diameter. It is important to determine specifically why a site needs improved drainage. Does the area contain plants that will be damaged it their roots are submerged? Is the area used for parking or recreation and must be useable even shortly after a rain? Answers to questions such as these will help determine how deep the pipe should be buried, how close together the laterals should be placed, and the pipe size and slope. The native soil is also a major factor in the system layout. Tight clay soils do not release groundwater as readily as looser sandy soils so a different layout will be required for a similar response.
Benefits of HDPE corrugated pipe in a subdrain system
• Variety ofpipe products available - Subdrain system requirements vary tremendously, often even on the same site. HDPE corrugated pipe producers manufacture pipe in diameters from 2- to 60-inch (50 to 1500 mm); with and without a smooth interior, perforations, and geotextile wrap; and a full line of fittings to meet just about any layout configuration. Most pipe is compatible with a variety of inlet structures. 
• Withstands traffic in minimum cover situations - Subdrains are sometimes installed relatively shallow where traffic, if present, creates the most force. Properly installed HDPE corrugated pipe can withstand AASHTO HS-25 loads with at least 1 ft (0.3 m) of cover for diameters 48-inch (1200 mm) and smaller, or 2 ft (0.6 m) for larger diameters.
• Withstands deep burials - Deep burials are not typical for subdrain systems. However, there may be occasions where the pipe will experience major soil loads especially if the ground is hilly or rolling. HDPE corrugated pipe can meet cover requirements of 20 ft (6 m) or more with proper backfill.
Corrugated HDPE - On The Job
The spring of 2002 marked the first full season for four brand new baseball fields in Everett, Washington, a city of 96,840 near Seattle. And since developers were starting from scratch, they didn’t hesitate to install a high-tech corrugated high-density polyethylene (HDPE) pipe drainage system in case any of the region’s 36 inches of yearly rainfall falls the night before the big game.
The Everett Park complex system, installed by Fuji Industries within a year, included a network of 4-inch perforated corrugated polyethylene pipe under each of the four diamonds. The design also called for drop “T” connections, to which 6-inch leader conveyance lines were attached. The 6-inch lines joined 8-inch pipes used under the parking lot, while 12-inch pipe was laid in the swale area. Each of the interconnected lines removes rainwater from the fields and surrounding areas and transports it to a 15-inch storm drainage system.
“What a great project – we built four Little League baseball diamonds over 13-acres of a former strip mine,” said Ryan Sass, PE, assistant park director for the Everett Parks and Recreation Department.. “The yearly demand for practice and game time means that kids have to play in the months of February, March and April during part of our wet season when rain is frequent. These fields allow them to do that more often.
Valve | PEX pipe | Push fit system | Plastic pipe | HDPE pipe | Water pipe
UPVC pipe | Spiral pipe | Gas pipe | Underground pipe | Polyethylene pipe fitting | Pipe installation
|